The following are a series of printing and print material definitions. Like all my other vocabulary posts, none of the definitions are in my own words nor are the photos used my own work. Everything used in this post was found on the internet and the definitions are referenced at the end of each term.
4-Color Printing: four different ink colors are used to create a range of printable colors. The “four-color” refers to the four color plates—cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (CMYK)—used in offset printing presses and most digital presses. These four colors are combined to make up a wide range of colors. source

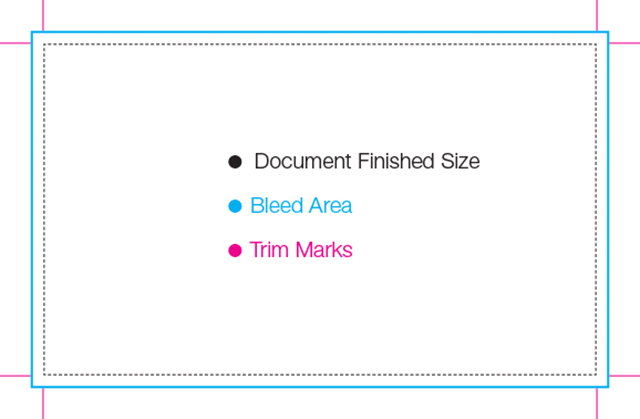
Bleed: used to describe a document which has images or elements that touch the edge of the page, extending beyond the trim edge and leaving no white margin. When a document has bleed, it must be printed on a larger sheet of paper and then trimmed down. source

Direct to Digital Printing: a printing method where the printing image is directly transferred from a printer onto a film, making this process highly flexible, environmentally friendly and offering high quality printing. source
Hard Proof: a preliminary version of a printed piece. It provides a close representation of how the piece will appear when printed. Proofs are created to ensure that the client and printer are in complete agreement on the desired outcome before going to press. source
Inkjet printing: the most common type of consumer printers. The inkjet technology works by spraying very fine drops of ink on a sheet of paper. These droplets are “ionized” which allows them to be directed by magnetic plates in the ink’s path. As the paper is fed through the printer, the print head moves back and forth, spraying thousands of these small droplets on the page. source

Letterpress: process by which many copies of an image are produced by repeated direct impression of an inked, raised surface against sheets or a continuous roll of paper. Letterpress is the oldest of the traditional printing techniques and remained the only important one from the time of Gutenberg, about 1450, until the development of lithography late in the 18th century and, especially, offset lithography early in the 20th. source

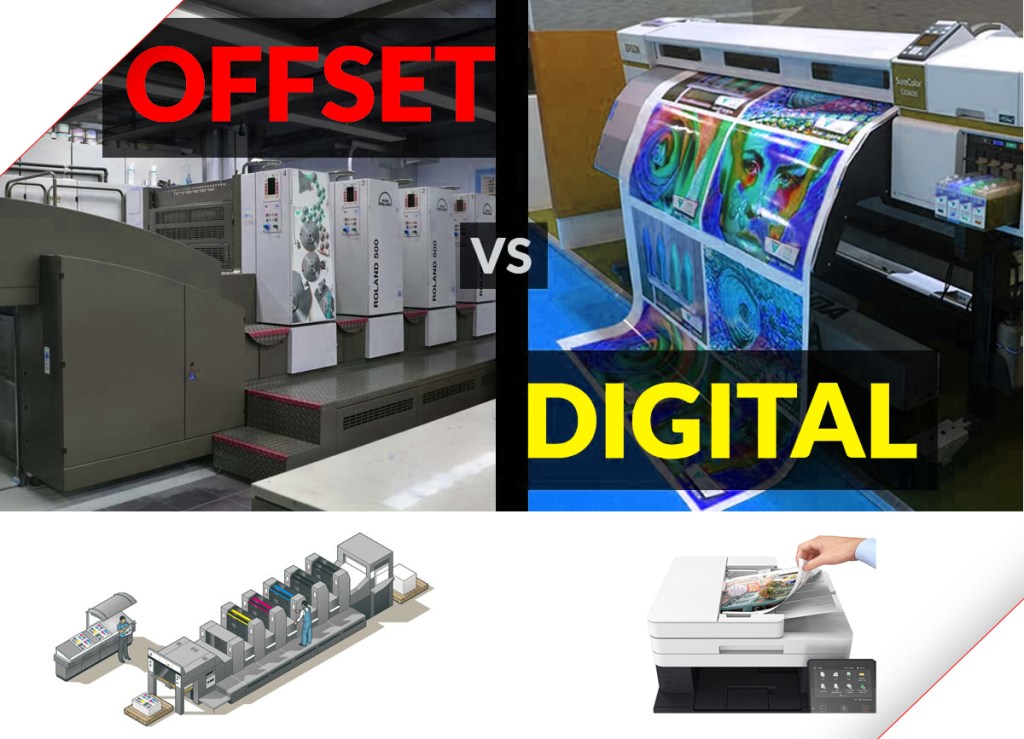
Offset Printing: uses plates, usually made from aluminum, which are used to transfer an image onto a rubber “blanket”, and then rolling that image onto a sheet of paper. It’s called offset because the ink is not transferred directly onto the paper. Because offset presses run so efficiently once they are set up, offset printing is the best choice when larger quantities are needed, and provides accurate color reproduction, and crisp, clean professional looking printing. source
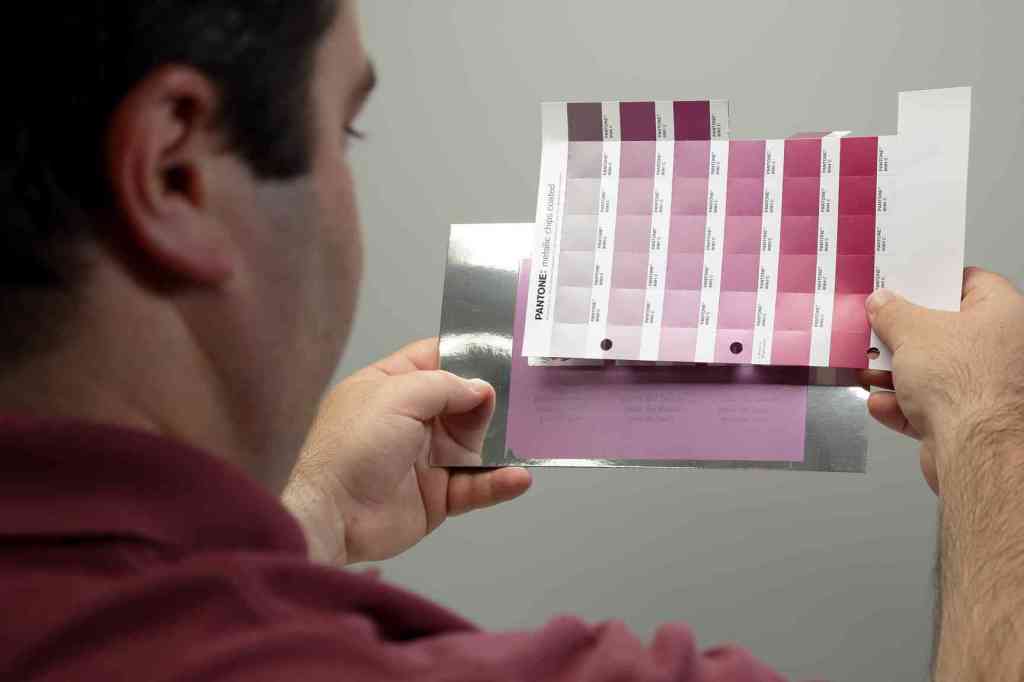
Pantone Colors: color codes that stand for a specific shade. You can communicate about colors by defining the pantone code. Basically, pantone is the standard language for colors. The formula developed by pantone is a spot color. This means that the color is created from a palette of 18 basic colors, not with screens or dots. Process colors are CMYK colors, the color is determined by cyan, magenta, yellow and black. There are more pantone colors because not all colors can be mixed in CMYK. source

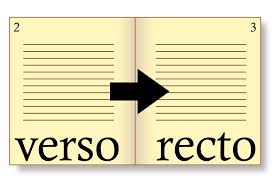
Recto / Verso: are respectively the “front” and “back” sides of a leaf of paper in a bound item such as a codex, book, broadsheet, or pamphlet. source
Screen Printing: a time-tested stenciling technique used to apply inked images to a wide variety of substrates. Using a stencil, or a series of stencils, the ink is distributed to the desired area(s) by being pressed through a porous screen, hence the name Screen Printing. source

Soft Proof: a mechanism that allows you to view on your computer monitor what your print will look like when it is on paper. A specific paper. That paper and ink combination has been defined by the profile that you or someone else has made for your printer / paper and ink combination. source

Substrate: the base material that the image will be printed on such a plastic film, glass, paper, canvas or other textile products. source
Trim: The final size of a printed page after excess edges have been cut off is the trim size. Crop marks indicating where to cut are printed at the edges of the paper that are then trimmed after printing. source
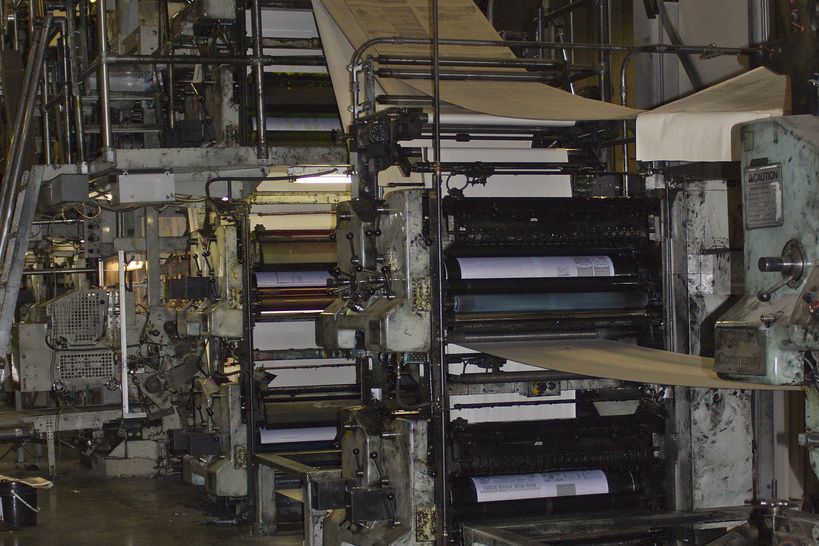
Web Press: a press that prints a continuous roll of paper. source
